The floodplains in the Amur River Basin create a corridor of wetlands, without which millions of migratory waterfowls could not reach their breeding grounds on the tundra at the Arctic shores. The China side of the Amur River Basin (CARB) only account for 45% of the whole area, however, it holds over 93% of the human population in this basin. Human settlements and agricultural developments in the CARB have severely affected floodplain wetlands.
A research team led by Prof. WANG Zongming from the Northeast Institute of Geography and Agroecology (IGA) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has revealed a dataset of long-term dynamics of floodplain wetlands over the CARB. The study was published in International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation.
Commonly, remote sensing data are directly used to obtain spatial distribution of wetlands. However, due to the complexity of wetland landscape, efficiencies and accuracies of wetland datasets were rarely low.
In this study, the research team used image compositing algorithm, Google Earth Engine, and big earth data to build robust image composites. And then, applied a hierarchical Random Forests (RF) classifier to obtain accurate classification results.
"The novelty of the method is that the study employed a hierarchical RF classification to get a two-category map at each node instead of using RF classifier to get a ten-category land cover map directly. Thus, the classification results derived from each node were extremely robust and accurate than traditional RF classifier." said Prof. WANG.
The study produced a 30-m resolution dataset that reflected dynamics of floodplain wetlands in the CARB during 1990–2018, with high mapping accuracies ( ranging from 90%±0.001 to 97%±0.005 ) .
Classification results indicated that from 1990 to 2018 floodplain wetlands decreased with a net rate of 25%. The lost wetlands were transformed mostly into paddy fields and dry farmlands.
"The agricultural activities were the dominant contributor to floodplain wetlands loss." said Prof. WANG.
The resultant dataset could provide reliable information for the efforts of floodplain wetland management, sustainable socio-economic development of floodplain, and support implementation of Sustainable Development Goals.
The research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Project.
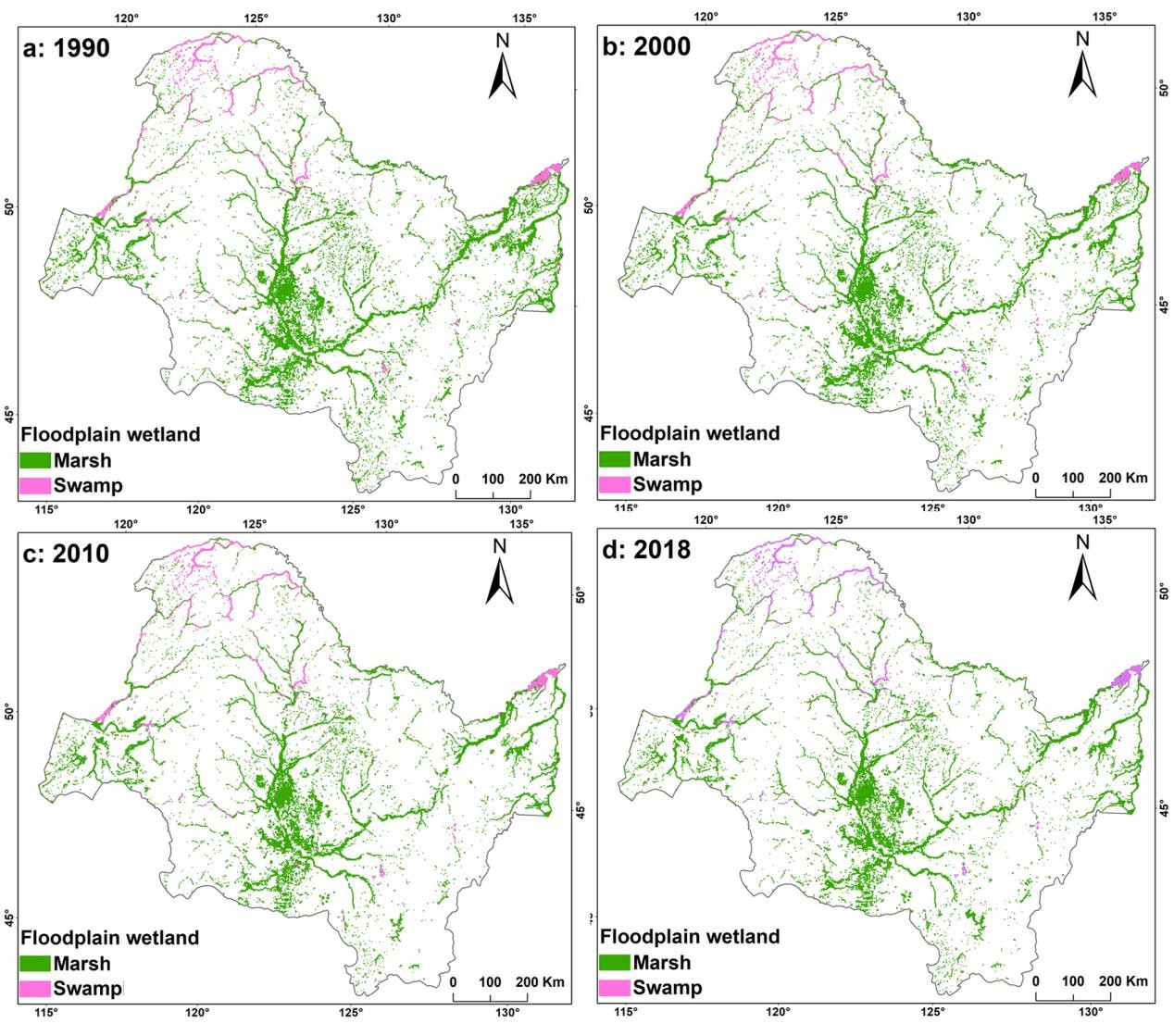
Spatial distributions of floodplain wetlands in the China side of the Amur River Basin (CARB) for the year of 1990, 2000, 2010, and 2018. (Imaged by Mingming JIA)
Contact:
Mingming Jia Associate Professor
Northeast Institute of Geography and Agroecology
E-mail: jiamingming@iga.ac.cn