Hyperspectral remote sensing is one of the frontier domains of remote sensing technology, which records ground objects’ spectral signature covering the visible to the infrared regions of the spectrum with tens of thousands of narrow bands. Such abundant spectral information provides a huge potential for the quantitative analysis of remote sensing data. Yet, it also poses a great challenge for data storage, management, processing and analysis. Thus, it is of paramount importance to reduce the dimensionality of hyperspectral images (HSI).
Recently, researchers at Northeast Institute of Geography and Agroecology of Chinese Academy of Sciences proposed a restrictive polymorphic ant colony algorithm (RPACA) based band selection algorithm (RPACA-BS) to reduce the dimensionality of hyperspectral images. In the proposed algorithm, both local and global searches were conducted considering band similarity. Moreover, the problem of falling into local optima, due to the selection of similar band subsets although travelling different paths, was solved by varying the pheromone matrix between ants moving in opposite directions.
(a) (b) (c)
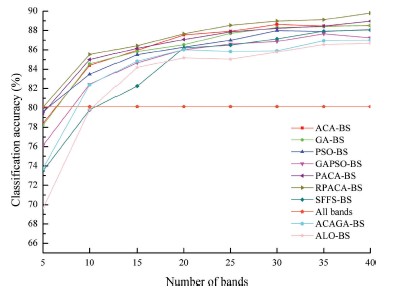
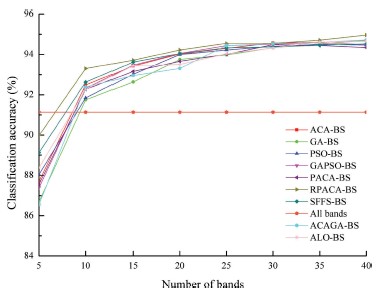
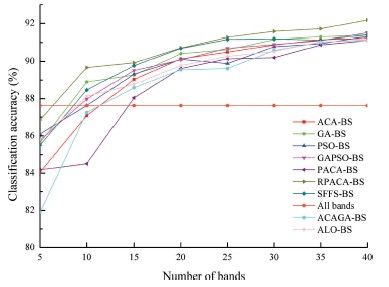
Fig. 1. The OAs of full-bands and the average OAs achieved by the band subsets with different sizes (5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35 and 40) selected from the Indian dataset (a), Pavia University dataset (b), and the Botswana dataset (c), respectively, by the ACA-BS, GA-BS, PACABS, PSO-BS, GAPSO-BS, SFFS-BS, RPACA-BS, ACAGA-BS and ALO-BS.
The performance of the proposed RPACA-BS algorithm was compared with a number of benchmarks, including the ant colony algorithm-based band selection algorithm (ACA-BS) and polymorphic ant colony algorithm-based band selection algorithm (PACA-BS), using three public datasets (the Indian Pines, Pavia University and Botswana datasets) based on average overall classification accuracy (OA) and CPU processing time. The experimental results showed that average OA of RPACA-BS was up to 89.80%, 94.96% and 92.17% for the Indian Pines, Pavia University and Botswana dataset, respectively, which was higher than that of the benchmarks. Meanwhile, the time consumed by RPACA-BS and PACA-BS were slightly lower than that of ACA-BS but obviously lower than that of other benchmarks. The proposed RPACA-BS method is thus able to effectively enhance the search abilities and efficiencies of the ACA-BS to handle the complex band selection issue for hyperspectral remotely sensed images.
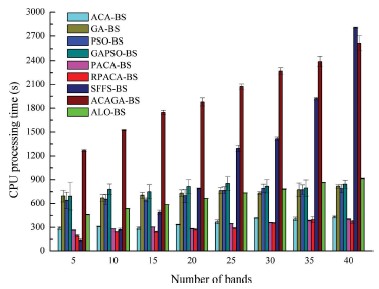
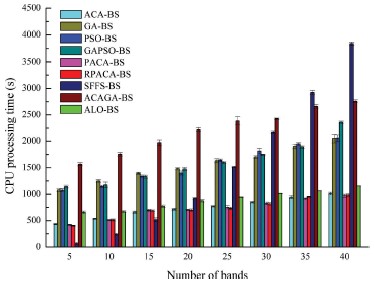
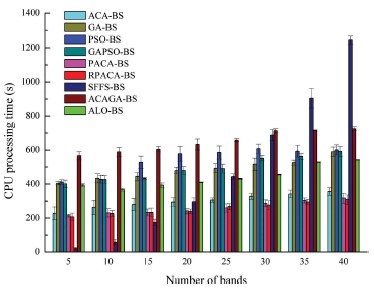
Fig. 2. The variations of the CPU processing time of the band selection algorithms when selecting band subsets from the Indian dataset (a), Pavia University dataset (b), and the Botswana dataset (c), respectively, with different sizes.
Reference:
Xiaohui Ding, Shuqing Zhang, Huapeng Li, Peng Wu, Patricia Dale, Lingjia Liu and Shuai Cheng. 2019. International Journal of Remote Sensing. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2019.1655810.
Contact:
LI Huapeng Ph.D.
Northeast Institute of Geography and Agroecology, CAS
Tel:85542230
E-mail:lihuapeng@iga.ac.cn